Couchbase
Summary
This document covers the information to gather from Couchbase in order to configure a Qarbine data service. The data service will use the Qarbine Couchbase driver. You can define multiple data services that access the same Couchbase endpoint though with varying credentials. Once a data service is defined, you can manage which Qarbine principals have access to it and its associated Couchbase data. A Qarbine administrator has visibility to all data services.
The example catalog components use data services named “Couchbase”, “Couchbase- beer”, “Couchbase- color”, and “Couchbase- travel”. To use them, create such data services with your settings as described below.
Overview
Couchbase is a NoSQL database which provides an SQL-like querying interaction. For details, see the Couchbase home page at https://couchbase.com.
Enabling Qarbine access to your cluster data involves the following steps:
- Determining the Couchbase URL and bucket,
- Adding or identifying a Couchbase user account and its password,
- Enabled IP access and
- Defining a Qarbine Data Service.
Couchbase Information
Endpoint
Navigate to your Couchbase console. For Couchbase Capella it is at
https://cloud.couchbase.com/
Information on adding users can be found at
https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/manage/manage-security/manage-users-and-roles.html
To locate your Couchbase URL navigate to the databases page by clicking
Click on the cluster of interest.
Click
Copy the public connection string
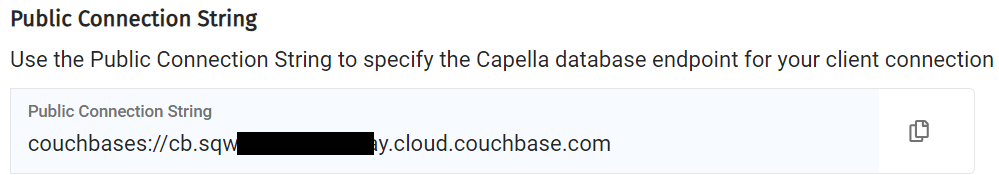
This value is used as the “server template” in the Qarbine data service.
Another DNS name of interest is the hostname shown below.
Database Account
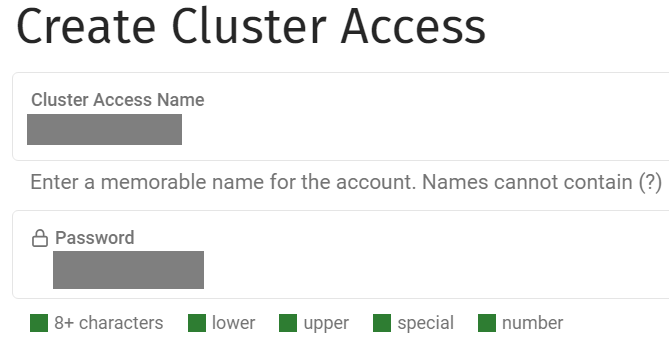
You should have identified a user account and its password for Qarbine readonly interactions. For reference shown below would be an example of creating a user with just these permissions. You may wish to limit bucket access as well based on your requirements.
For more details see https://docs.couchbase.com/cloud/clusters/manage-database-users.html.
A starting page on the Capella console for managing cluster access is at https://cloud.couchbase.com/database/settings/access-control
Below is an example of a cluster access account.
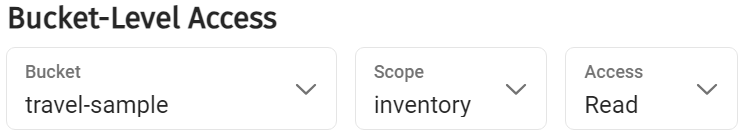
The bucket level access should be done for each of the buckets for the given user.
More information is below. Once satisfied click
Buckets and Scopes
Conceptually,
- Buckets map to SQL databases,
- Scopes map to SQL schemas, and
- Collections map to SQL tables.
To see your buckets navigate to the Couchbase cluster tab shown below.
Couchbase Sample Buckets
Couchbase provides several data sets to quickly start interacting with Capella. The Qarbine samples in the “example/Couchbase” folder reference the data services named “Couchbase- XXX”. This Couchbase page provides some background on the sample data.
https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/manage/manage-settings/install-sample-buckets.html
To load it, log in to Capella and navigate to the cluster of interest.
Click
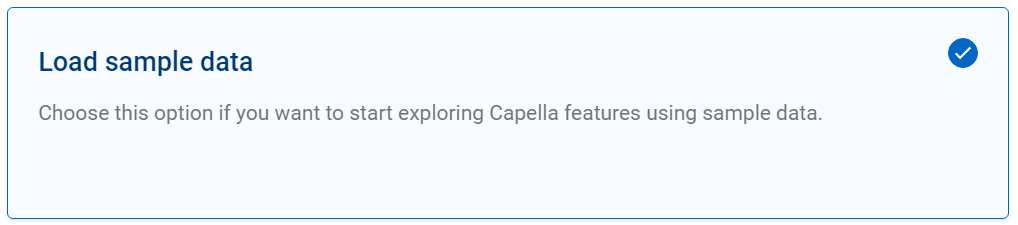
For each data set of interest select it and then click.
Below is an example snapshot after some of the data sets are loaded.
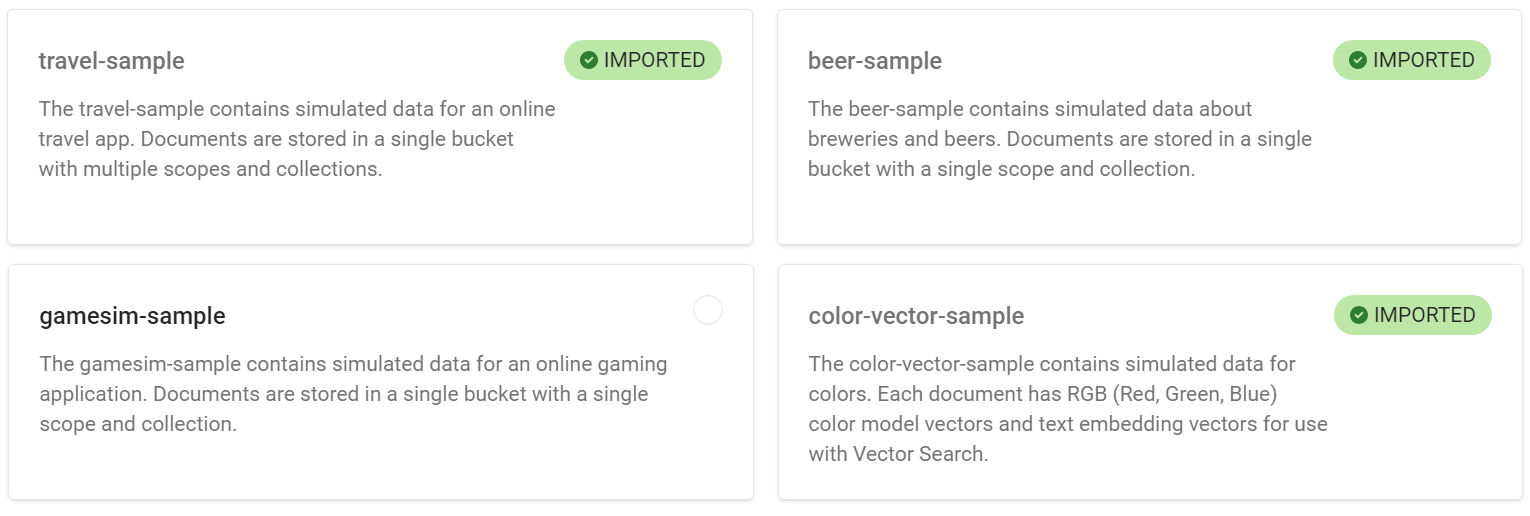
The left hand side panel displays some of the examples loaded.
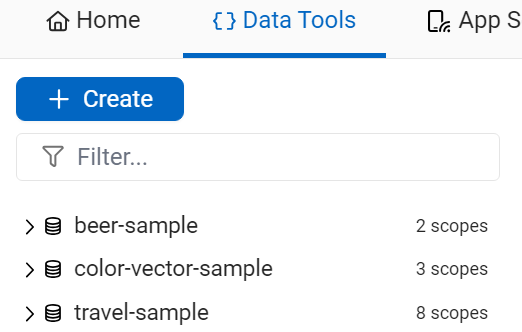
Expanding the first bucket shows

Expanding the second bucket shows

Expanding the third bucket shows
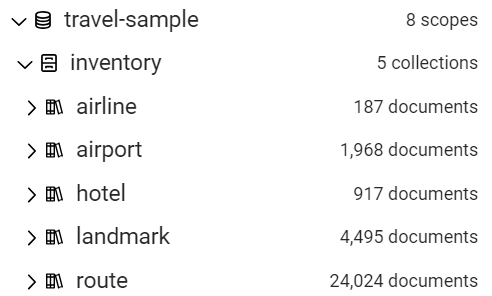
Identify the scope of interest for each bucket. Usually there is just one, well-named scope that is the one to use for Qarbine querying. The Qarbine database value described below is formatted with the bucket name, a space, and the scope name.
| Bucket | Scope of Interest | Qarbine “Database” value |
|---|---|---|
| beer-sample | _default | beer-sample _default |
| color-vector-sample | color | color-vector-sample color |
| travel-bucket | inventory | travel-bucket inventory |
The Qarbine catalog has examples for the 3 buckets above. There are also 3 corresponding data services defined, one for each of the buckets.
NOTE - Each of these 3 Couchbase data services must be configured to reference your Couchbase cluster containing the sample bucket data as described below. They must also be enabled by choosing the option shown below.
When the Qarbine data service’s database field is empty, you will have to fully qualify the collection path in your queries with Bucket.Scope.Collection. If there are dashes in any of the pieces then use tick marks to enclose the string. For example, `travel-sample`.inventory.hotel.
If a user tries to run an example and that data service references data it doesn't have permission for then an error will be returned. An example is shown below.
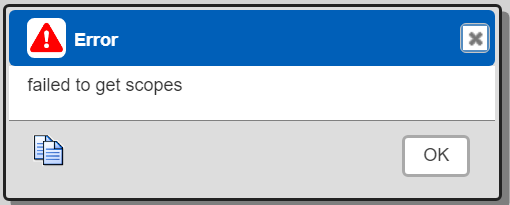
Allowing an IP address
Add the Qarbine host IP address to the cluster’s list of allowed IPs using the information at
Access this area by clicking the highlighted sidebar item shown below.
Qarbine Data Service Configuration
Overview
The Qarbine data service requires
- Qarbine compute node URL,
- Couchbase URL,
- Couchbase user and password, and
- Couchbase default bucket.
Compute Node Preparation
Determine which compute node service endpoint you want to run this data access from. That URL will go into the Data Service’s Compute URL field. Its form is “https://domain:port/dispatch”. A sample is shown below.
The port number corresponds to a named service endpoint configured on the given target host. For example, the primary compute node usually is set to have a ‘main’ service. That service’s configuration is defined in the ˜./qarbine.service/config/service.main.json file. Inside that file the following driver entry is required
"drivers" :[
. . .
"./driver/couchbaseDriver.js"
]
The relevant configuration file name for non primary (main) Qarbine compute nodes is service.NAME.json. Remember to have well formed JSON syntax or a startup error is likely to occur. If you end up adding that entry then restart the service via the general command line syntax
pm2 restart <service>
For example,
pm2 restart main
or simply
pm2 restart all
Defining the Qarbine Data Service
Open the Administration Tool.
Navigate to the Data Services tab.
A data service defines on what compute node a query will run by default along with the means to reach to target data. The latter includes which native driver to use along with settings corresponding to that driver. Multiple Data Sources can reference a single Data Service. The details of any one Data Service are thus maintained in one spot and not spread out all over the place in each Data Source. The latter is a maintenance and support nightmare.
To begin adding a data service click
Enter the name, description, and Qarbine compute node endpoint URL.
Choose
For the server template enter
couchbases://THE_COPIED_URL_FROM_ABOVE
For the server options enter
userName="THE_USER",
password="THE_PASSWORD",
configProfile = "wanDevelopment"
Optionally you may specify options such as:
- consoleLogLevel
- ssl (the default is “no_verify”)
- tls_verify=none
- kvTimeout
- kvDurableTimeout
- viewTimeout
- queryTimeout
- analyticsTimeout
- searchTimeout
- managementTimeout
Information about server options is available by clicking the icon shown below.
You can reference environment variables using the syntax %NAME%. Any strings should be quoted and the key\value pairs separated by commas. For further information see
https://docs.couchbase.com/go-sdk/current/howtos/troubleshooting-cloud-connections.html
https://docs.couchbase.com/nodejs-sdk/current/ref/client-settings.html
The “database” field here maps to a Couchbase bucket and scope name with a space separator as described above.
When the Qarbine data service’s database field is empty, the query author will have to fully qualify the collection path in your queries with Bucket.Scope.Collection. If there are dashes in any of the pieces then tick marks are used to enclose the string. For example, `travel-sample`.inventory.hotel.
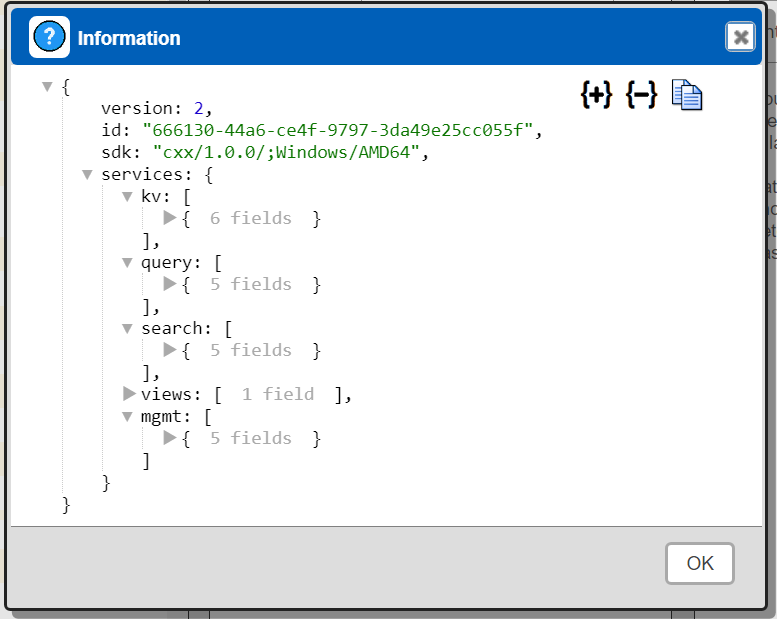
Next, test the settings by clicking on the icon noted below.
You should see the following general dialog
Save the Data Service by clicking on the image highlighted below.
The data service will be known at the next log on time.
Data Service Query Interactions
For retrieving data from Couchbase, Qarbine supports using a JSON specification. The format is
{
useSearch: true | false,
bucket: aString,
scope: aString,
index: aString, ← required.
other fields per Couchbase documentation
}
This is primarily used with vector searches. See
https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/search/search-request-params.html
You can access all of these options using SQL++ though which is the recommended approach. See https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/search/run-searches.html#sql
The useSearch flag above determines whether the search or query endpoint is used. The configured Qarbine Data Service’s server template prefix (couchbase:// vs couchbases://) determines whether the HTTPS secure endpoint is used. The cbHostName value is the text after couchbase(s):// in the server template. A sample secure server template is
couchbases://cb.abcdefghijk.cloud.couchbase.com
Its cbHostName is
cb.abcdefghijk.cloud.couchbase.com
| Protocol | Type | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | query | http://${cbHostName}:8093 |
| search | http://${cbHostName}:8094 | |
| HTTPS | query | https://${cbHostName}:18093 |
| search | https://${cbHostName}:18094 |